SSL/TLS Operation Layer
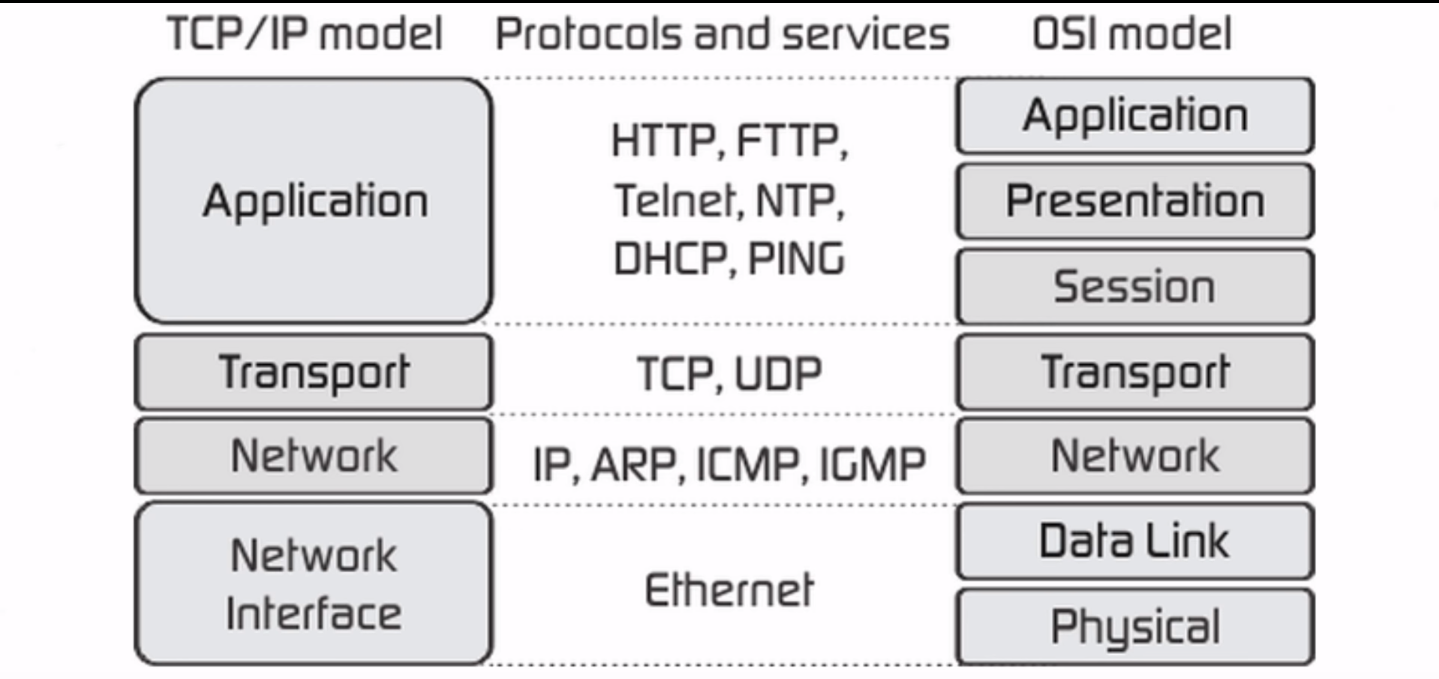
The SSL/TLS protocol operates on:
- Application / Presentation / Session layers of OSI model
- Application layer of TCP/IP model
SSL/TLS Handshake Process
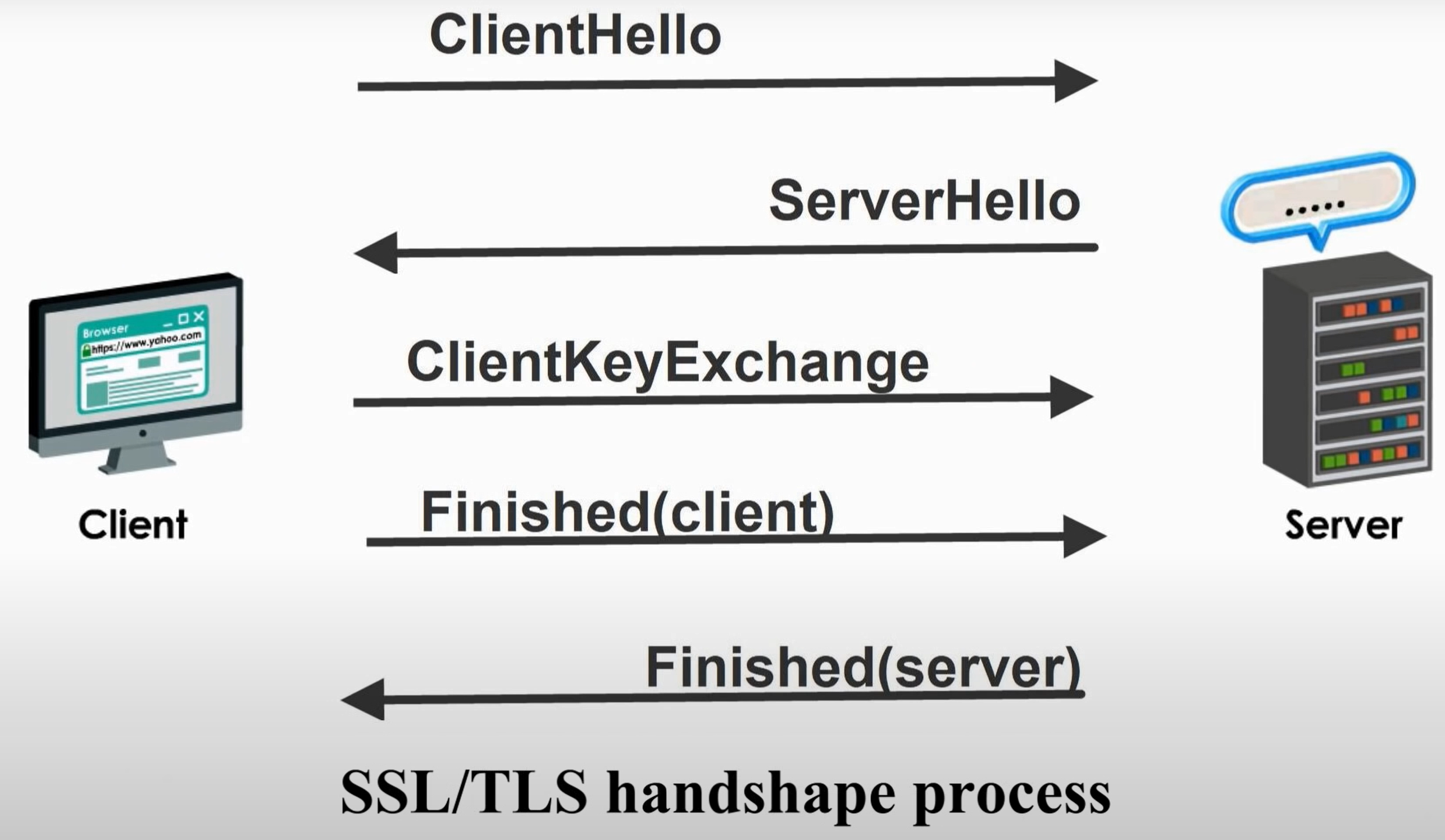
Step 1 ClientHello

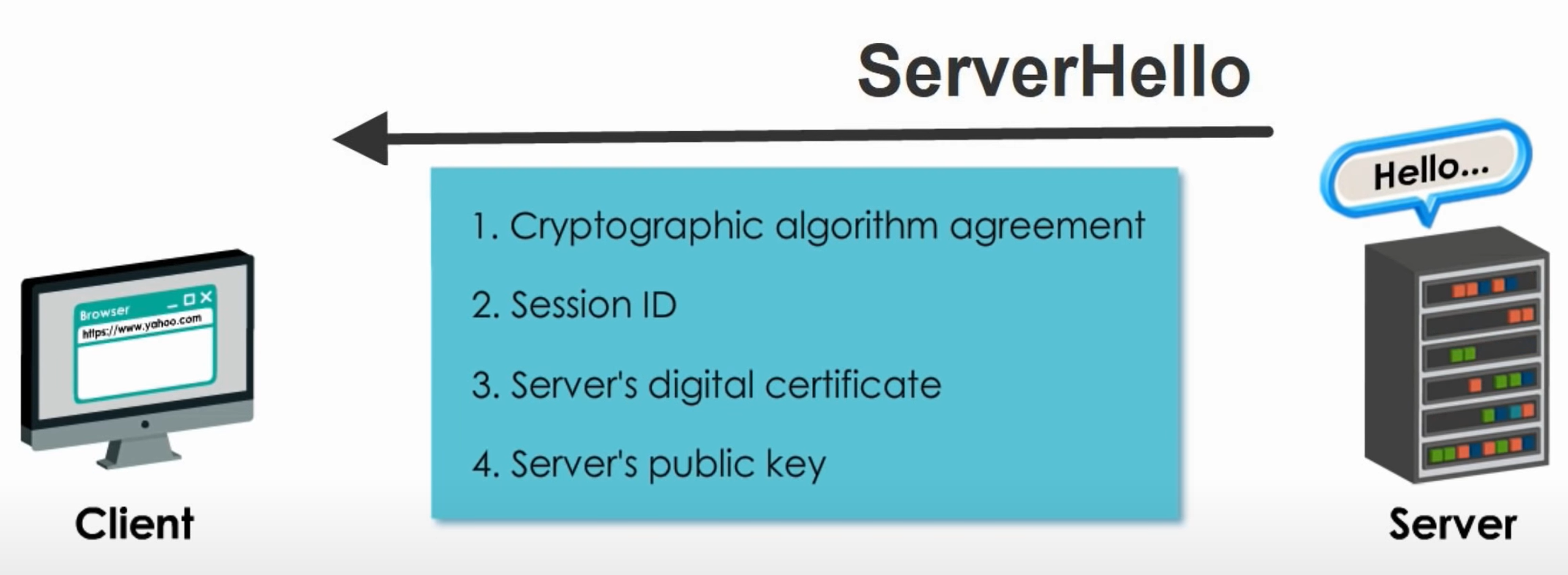
Step 2 ServerHello
Step 3 Verify Digital Certificate

The client will contact the server’s CA(certificate authority) and verify the server’s digital certificate, thus confirming the authenticity of the web server.
GOAL: Establishing the trust on the web server.
Step 4 ClientKeyExchange

Step 5 Finished(client)

Step 6 Finished(server)

Step 7 Handshake Done. Exchanged Message

Once the handshake is done, the server and client can now exchange messages that are symmetrically encrypted with the shared secret key.
Notes
- The above process demonstrates how asymmetric key algorithm and symmetric key algorithm work together.
- Asymmetric key algorithm (public key & private key) is used to verify the identity of the owner and its public key so that trust is built.
- Once the connection is established, Symmetric key algorithm (shared key) is used to encrypt and decrypt all traffic between them.
The green padlock: indicates that the web server’s public key really belongs to the web server, not someone else.
The
Httpsand the green padlock only indicates the communications between client and server are encrypted. It does not says the website is “safe and good”.