The UML Class diagram is a graphical notation used to construct and visualize object oriented systems. A class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system’s:
- classes
- their attributes
- operations (or methods)
- and the relationships among objects.
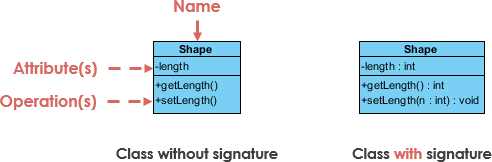
UML Class Notation
A class represent a concept which encapsulates state (attributes) and behavior (operations). Each attribute has a type. Each operation has a signature. The class name is the only mandatory information.
Class Visibility
The +, - and # symbols before an attribute and operation name in a class denote the visibility of the attribute and operation.
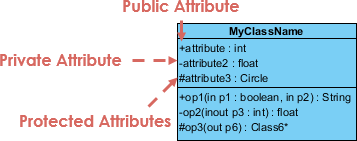
+denotes public attributes or operations-denotes private attributes or operations#denotes protected attributes or operations
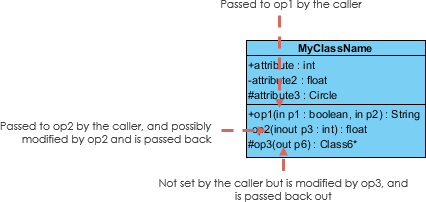
Parameter Directionality
Each parameter in an operation (method) may be denoted as in, out or inout which specifies its direction with respect to the caller. This directionality is shown before the parameter name.
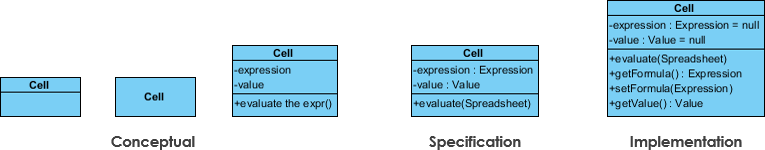
Perspectives of Class Diagram
The choice of perspective depends on how far along you are in the development process. During the formulation of a domain model, for example, you would seldom move past the conceptual perspective. Analysis models will typically feature a mix of conceptual and specification perspectives. Design model development will typically start with heavy emphasis on the specification perspective, and evolve into the implementation perspective.
A diagram can be interpreted from various perspectives:
- Conceptual: represents the concepts in the domain
- Specification: focus is on the interfaces of Abstract Data Type (ADTs) in the software
- Implementation: describes how classes will implement their interfaces
The perspective affects the amount of detail to be supplied and the kinds of relationships worth presenting. As we mentioned above, the class name is the only mandatory information.
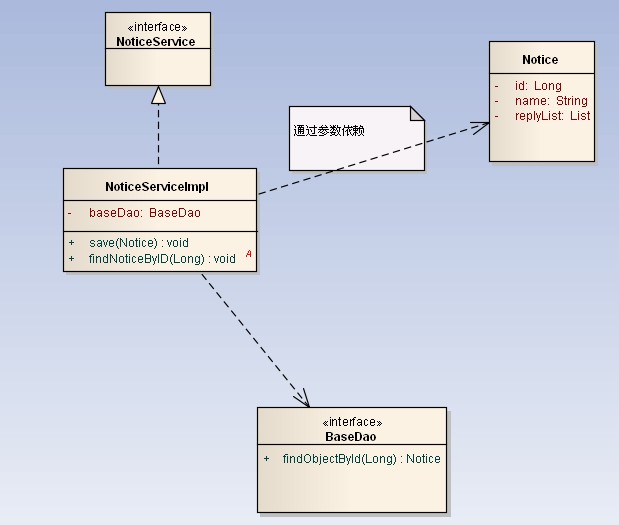
Relationships between classes
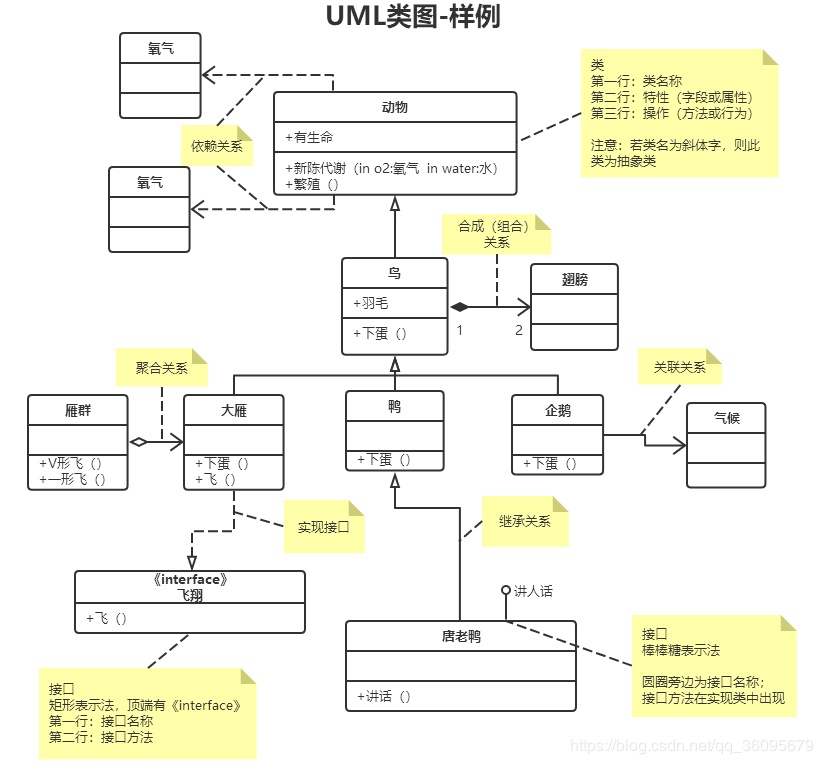
类的关系有泛化(Generalization)、实现(Realization)、依赖(Dependency)和关联(Association)。其中关联又分为一般关联关系和聚合关系(Aggregation), 合成关系(Composition)。
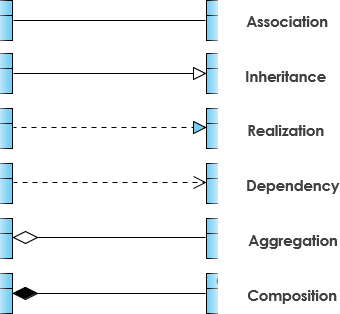
虚线箭头指向依赖;
实线箭头指向关联;
虚线三角指向接口;
实线三角指向父类;
空心菱形能分离而独立存在,是聚合;
实心菱形精密关联不可分,是组合;
泛化(generalization) :表示 is-a 的关系,是对象之间耦合度最大的一种关系,子类继承父类的所有细节。直接使用语言中的继承表达。在类图中使用带三角箭头的实线表示,箭头从子类指向父类。
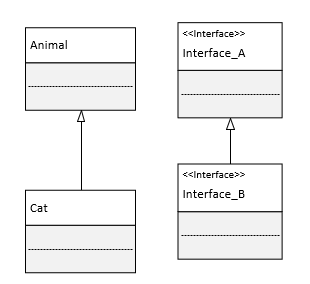
- An abstract class name is shown in italics.
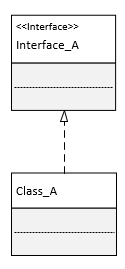
实现(Realization):在类图中就是接口和实现的关系。在类图中使用带三角箭头的虚线表示,箭头从实现类指向接口。
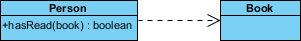
依赖(Dependency) :对象之间最弱的一种关联方式,是临时性的关联。代码中一般指由局部变量、函数参数、返回值建立的对于其他对象的调用关系。一个类调用被依赖类中的某些方法而得以完成这个类的一些职责。在类图使用带箭头的虚线表示,箭头从使用类指向被依赖的类。
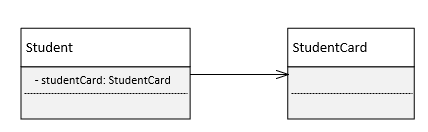
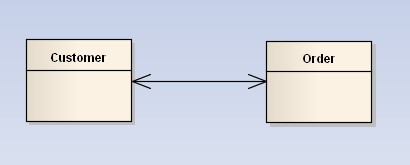
关联(Association): 对象之间一种引用关系,比如客户类与订单类之间的关系。这种关系通常使用类的属性表达。关联又分为一般关联、聚合关联与组合关联。
一般关联。在类图使用带箭头的实线表示,箭头从使用类指向被关联的类。可以是单向和双向。
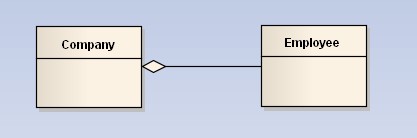
聚合(Aggregation) :表示 has-a 的关系,是一种不稳定的包含关系。较强于一般关联,有整体与局部的关系,并且没有了整体,局部也可单独存在。如公司和员工的关系,公司包含员工,但如果公司倒闭,员工依然可以换公司。在类图使用空心的菱形表示,菱形从局部指向整体。
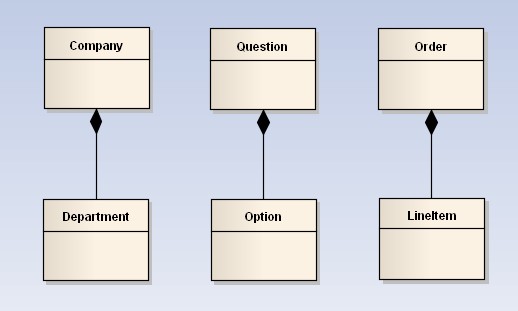
组合(Composition) :表示 contains-a 的关系,是一种强烈的包含关系。组合类负责被组合类的生命周期。是一种更强的聚合关系。部分不能脱离整体存在。如公司和部门的关系,没有了公司,部门也不能存在了;调查问卷中问题和选项的关系;订单和订单选项的关系。在类图使用实心的菱形表示,菱形从局部指向整体。
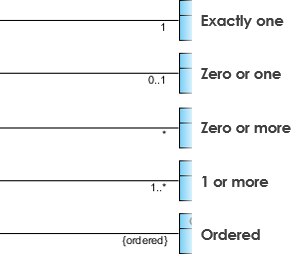
Cardinality is expressed in terms of:
- one to one
- one to many
- many to many
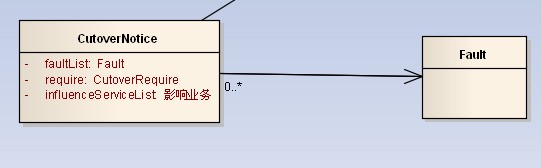
多重性(Multiplicity) : 通常在关联、聚合、组合中使用。就是代表有多少个关联对象存在。使用数字..星号(数字)表示。如下图,一个割接通知可以关联0个到N个故障单。
Relationship Discrimination
聚合和组合的区别
聚合关系是“has-a”关系,组合关系是“contains-a”关系;聚合关系表示整体与部分的关系比较弱,而组合比较强;聚合关系中代表部分事物的对象与代表聚合事物的对象的生存期无关,一旦删除了聚合对象不一定就删除了代表部分事物的对象。组合中一旦删除了组合对象,同时也就删除了代表部分事物的对象。
依赖和关联的区别
依赖(Dependency)
从字面理解的话,是说一个类用到了另一个类。这种使用关系是具有偶然性的、临时性的、非常弱的。比如下图中的依赖关系,司机开车,要依赖车。在代码上表现的话一般为函数参数,或者局部变量或者对静态方法的调用。注意依赖关系只能是单向的,并且依赖关系强调的是 使用上的关系。
关联(Association)
- 关联关系强调的是一种结构上的关系
- 他可以是单向的或者双向的
- 从语义级别(上下文)可以分为聚合和组合,在代码实现上关联和聚合是很像的,主要区别在语义上
- 一般来说双方关系是平等的,比如我和我的朋友
- 在java语言上一般表现为全局变量。如person类和company类,顾客和地址,客户和订单
Example
Software to Draw UML Class Diagram
- Visio
- Enterprise Architect
- Rose