
Unit 1: Overview of Node.js Learning Path
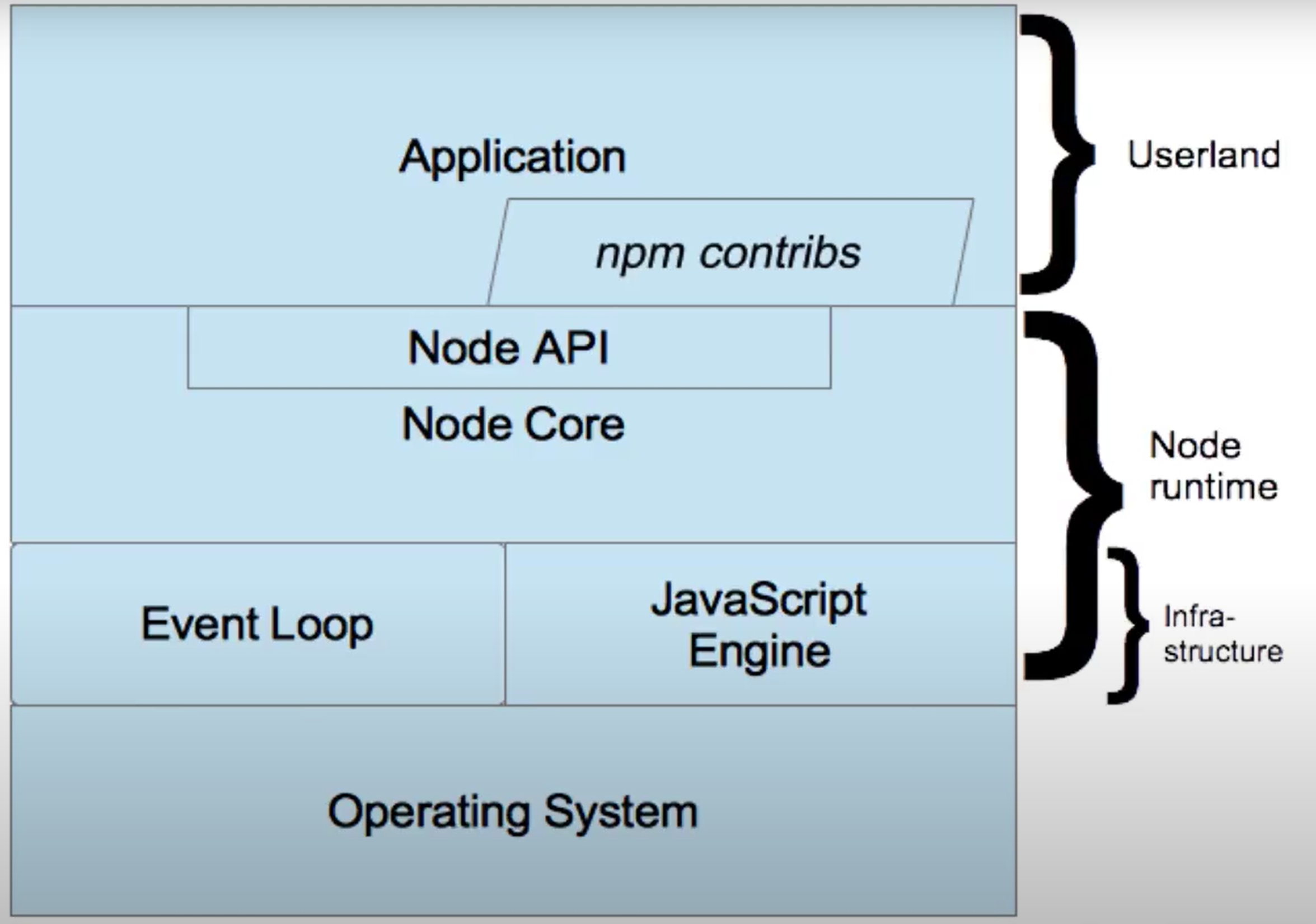
- Node Architecture
- Libuv.org
- node modules
- Overview of Blocking vs Non-Blocking
- Easy profiling for Node.js Applications
Unit 2: Installing Node.js, npm, and VSCode
Install Node and Npm
Install from nodejs.org
Unit 3: A tour of Node.js
Node.js Architecture
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome V8 JavaScript engine.

- JavaScript Engine: Chrome V8
- Event Loop: libuv
- Node.js API: https://nodejs.org/docs/latest/api/
ECMAScript Standard
Read-Eval-Print-Loop (REPL)
npm
npm consists of:
- the website: https://www.npmjs.com
- the CLI
- the registry
Unit 4: Node.js basic concepts
Node Modules
In the Node.js module system, each file is treated as a separate module.
- Built-in Modules
- Installed Modules from https://www.npmjs.com/
- Customized Modules
Non-blocking I/O
Overview of Blocking vs Non-Blocking
Load Testing
-
1
loadtest -c 10 --rps 200 http://mysite.com/
Consider case where each request to a web server takes 50ms to complete and 45ms of that 50ms is database I/O that can be done asynchronously. Choosing non-blocking asynchronous operations frees up that 45ms per request to handle other requests. This is a significant difference in capacity just by choosing to use non-blocking methods instead of blocking methods.
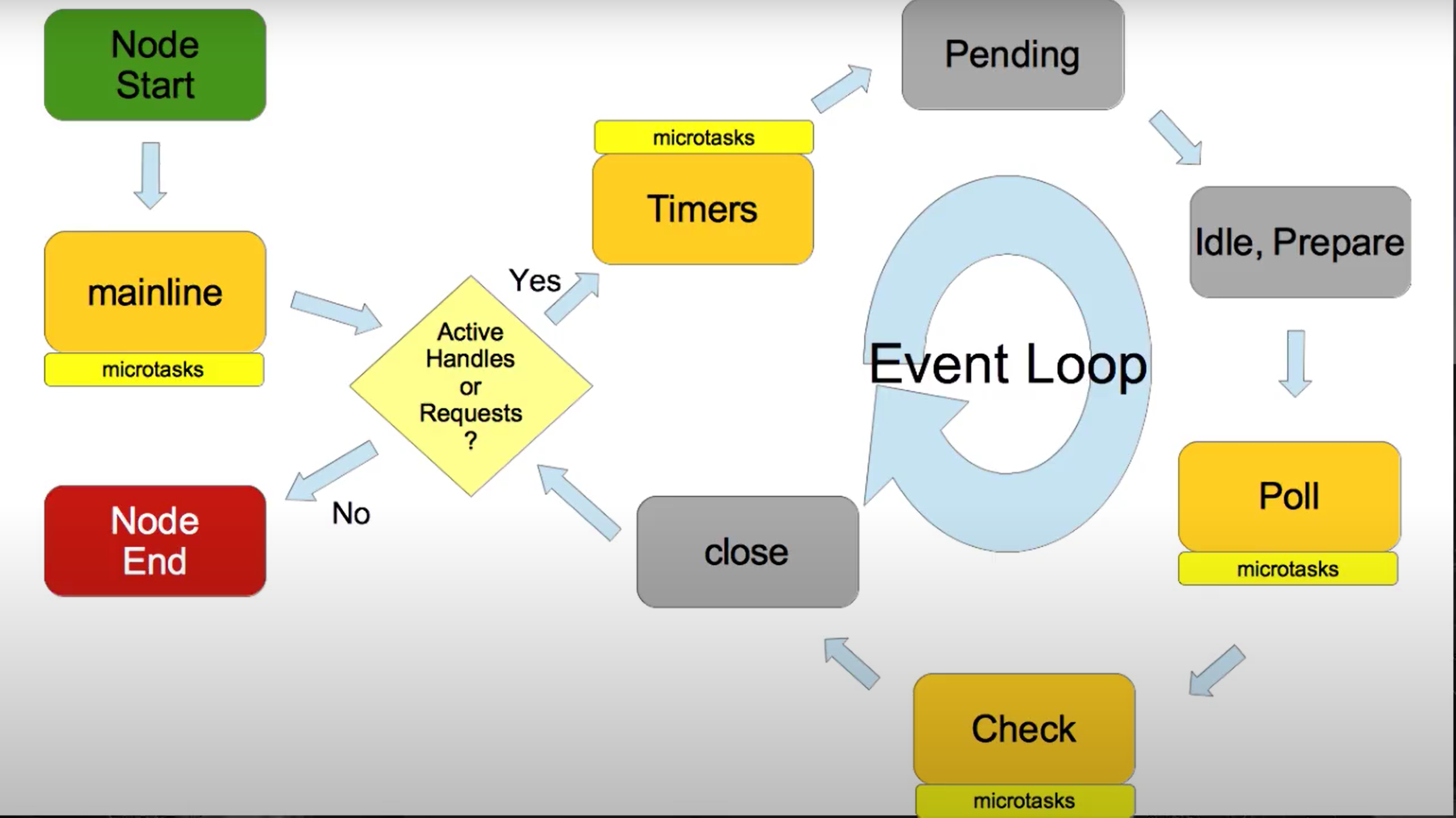
Unit 5: The event loop
A complete guide to the Node.js event loop
Unit 8: Node dependency management
Semantic version (semver)
- npm semver calculator: https://semver.npmjs.com/
- caret (aka hat) symbol,
^: include everything that does not increment the first non-zero portion of semver.1
"^2.1.9": >= 2.1.9 and < 3.0.0
- tilde symbol,
~: include everything greater than a particular version in the same minor range.1
"~2.1.9": >= 2.1.9 and < 2.2.0
Visualization of npm dependencies: http://npm.anvaka.com/
Unit 9: Unit testing and linting with Node.js
There are two aspects to code quality that you can automate.
- Testing
- Linting
- A linter with parser [ESlint]
- A configuration to apply rules to your code
How to Test NodeJS Apps using Mocha, Chai and SinonJS
Unit 10: Application logging with Winston and Log4js
Application logging is a reality that we as developers have to deal with, and it isn’t going anywhere. When our applications run, things happen. Some of those things are important. Others are not.
Logs tell us what happened and are useful when supporting our applications. console.log() is fine for prototypes, but for production quality applications, you need production quality logging.
You can write this code yourself, but the logging problem has been solved.
Two popular third party logging packages for Node applications
Logging Example on GitHub: link
Unit 11: ExpressJS and Pug
- ExpressJS: for a web framework, which includes routing.
- Pug: for the user interface.
ExpressJS and Pug Example on GitHub: link
Unit 12: MongoDB
MongoDB is one of the most popular choices for storing data used with Node applications.
